Table of contents
Why do You Get a Referral for Physical Therapy After Excision Surgery?
- Endometriosis is a chronic condition and it takes almost 10 years to diagnose the condition in most cases.
- The women suffer from severe pain and disability before they are really diagnosed with endometriosis. Pain leads to muscle guarding and spasms which leads to further limitation in mobility and function.
- Muscle guarding can also affect fascial mobility. Fascia covers our body from head to toe, it covers the muscles and organs and connects muscle to muscle and muscle to organ. Any fascial restrictions can affect the mobility of the organ and body and also function.
- Decreased mobility can affect the circulation and lymphatic draining. Many women present with blood stasis and swelling of pelvic region- vulva, discoloration and sometimes itching.
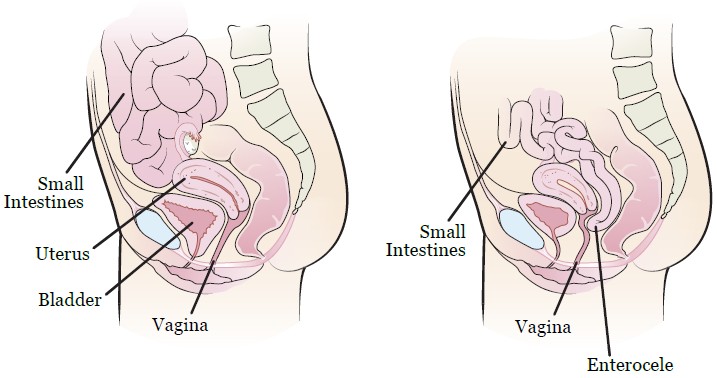
- Some women with endometriosis can present with the descend of a small intestine between uterus and rectum and it pushes the wall of vagina, it is called “enterocele”.
- Surgery can lead to scar tissue and muscle guarding which can affect the normal biomechanical movement.
- Many women have pain and pelvic floor dysfunction after surgery which can affect the function.
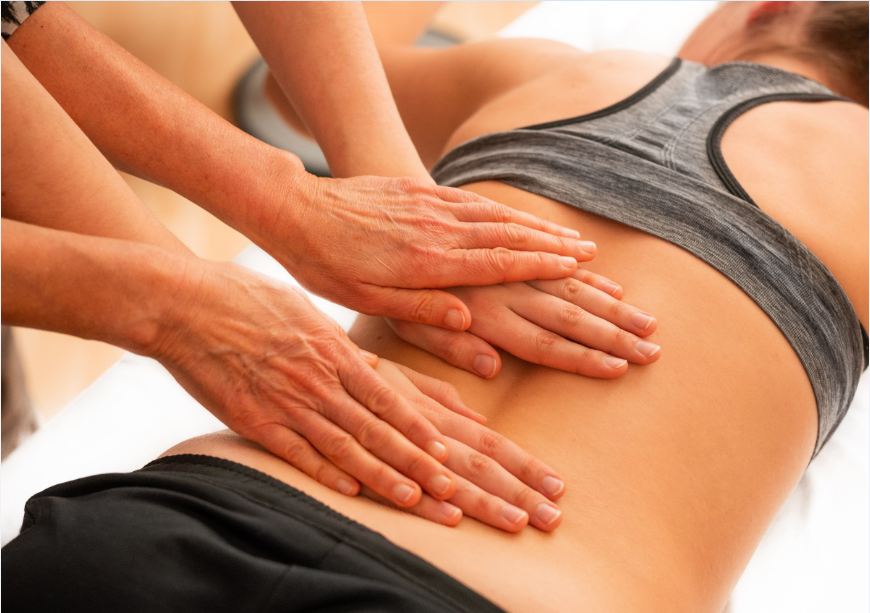
How does Fascial Mobility Affect the Pelvic Floor Function?
- Facia lines from Amygornall.com
- The abdominal fascial restrictions from guarding can affect the mobility of the fascia of the large and small intestine. Scar tissue after surgery can also affect the abdominal fascial mobility.
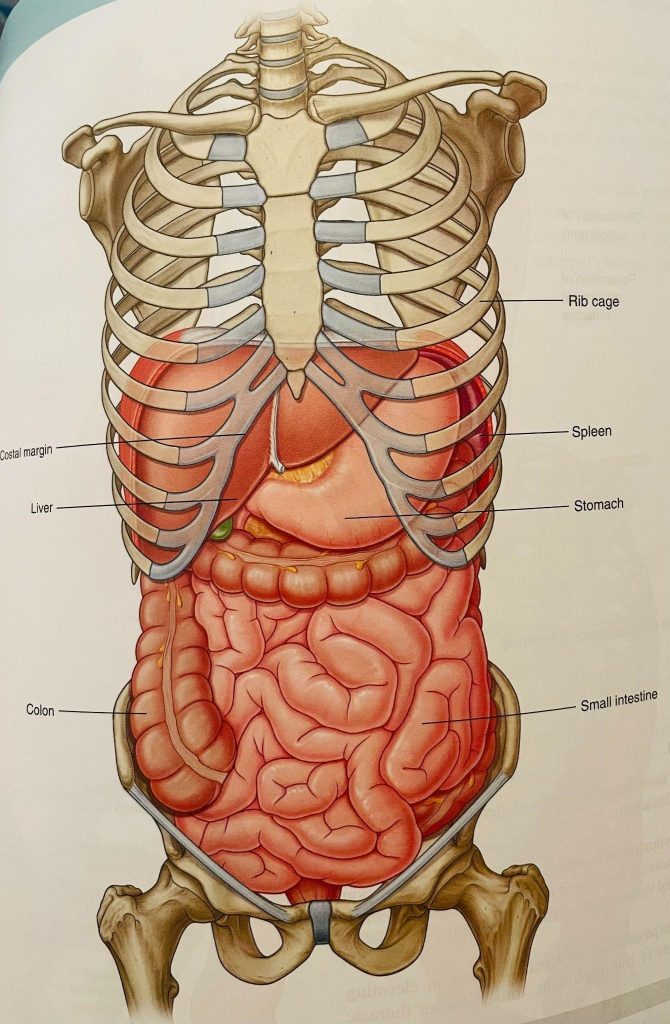
- This is image is taken from Grey’s Anatomy
- The restrictions of the fascia around cecum (ascending colon on right side) and sigmoid colon (descending colon on left side) can affect bowel movement- many women have constipation, diarrhea, pain after bowel movement, bloating, and food intolerance. Constipation is defined as
- Small palates, hard stools, straining
- Not able to empty bowels completely
- Less than 3 spontaneous bowel movements a week
- The patient has to do manual maneuver to pass the stool
- Straining with stools can lead to pelvic floor dysfunction and increase the risk of prolapse
- Bristol stool scale helps to understand the consistency of stool and relation to constipation. As if you have bowel movement everyday does not mean you are not constipated. Bristol stool scale 1-2 is considered as constipation, 3-4 is considered as normal bowel movement as long as the person is not straining while doing bowel movement, 5-7 is considered as diarrhea

The restrictions of fascia around the bladder can cause
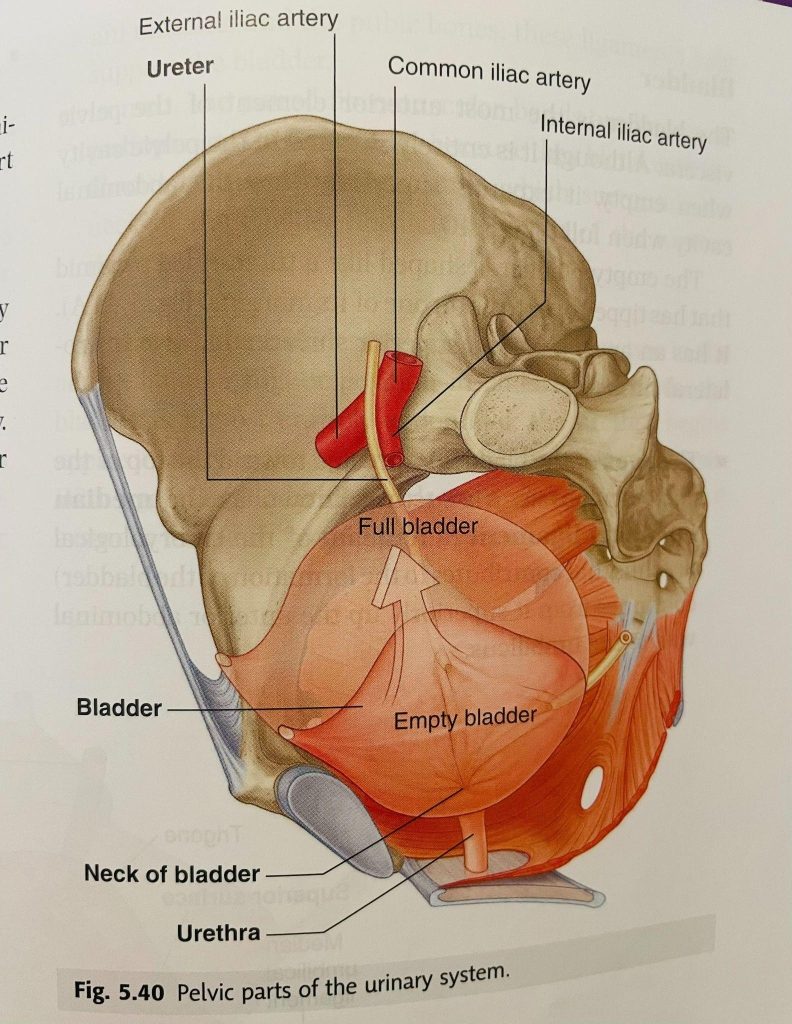
The image is taken from Grey’s Anatomy
- Increase in urinary urgency and frequency
- Bladder fascia shares the fascia with pelvic floor through urethra and it can cause stress/urge or both urinary incontinence.
- Bladder fascia also shares the fascia with obturator foramen where obturator internus muscle attaches. Obturator internus muscle is one of the major rotator muscles of the hip. Restrictions of bladder fascia can affect the mobility/mechanics of the hip and also can cause pain. Many women with hip pain without any pathology might have a connection to the bladder fascia. They always have one of the bladder symptoms such as urgency/frequency/burning of urination or incontinence.
- Anatomically small intestine sits on the bladder. The small intestine moves up and allows the bladder to fill. If the fascial mobility of the small intestine is limited or if the small intestine has descended, the bladder does not get enough room to fill and that leads to increase in urgency and frequency.
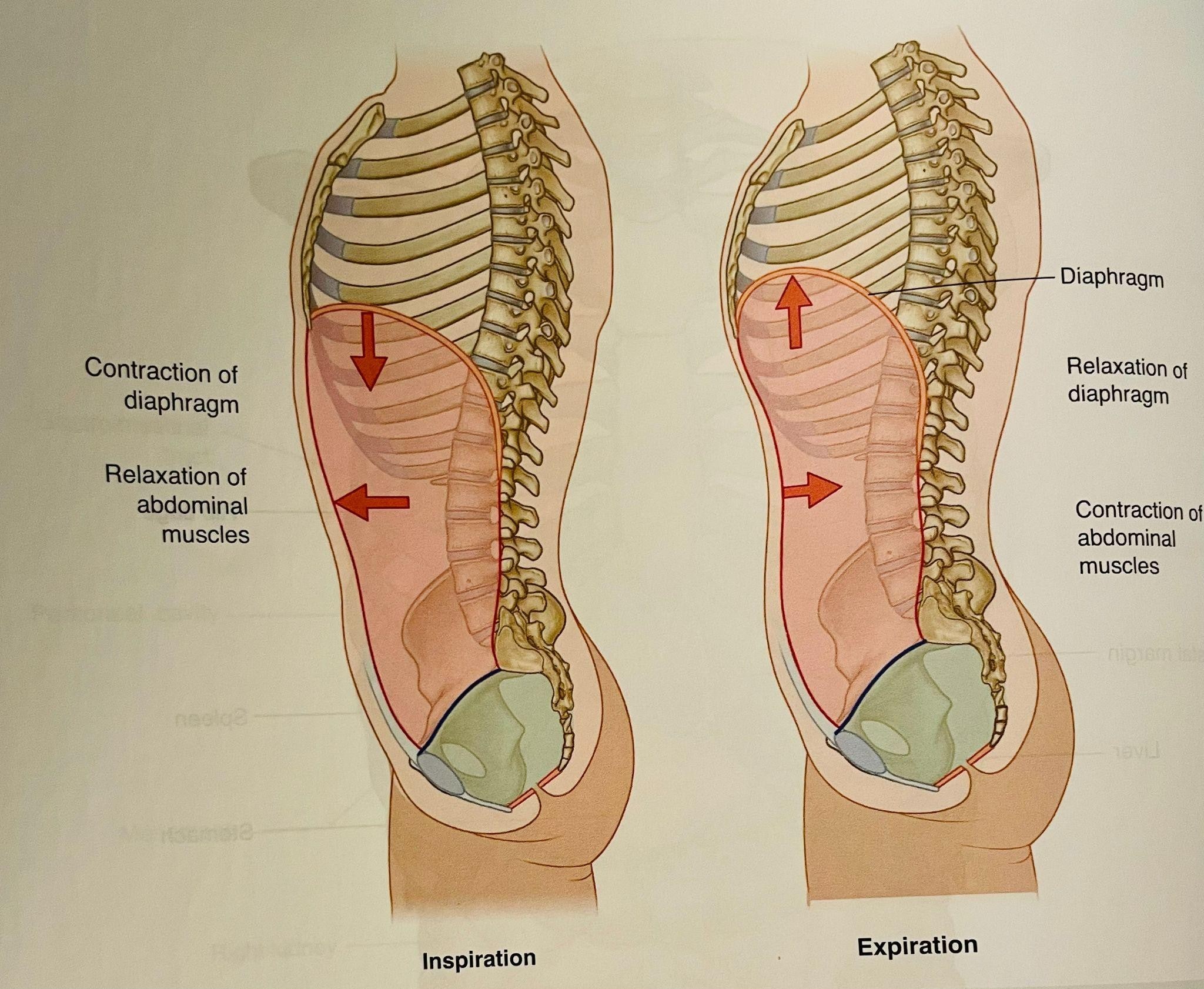
- The image is taken from Sloan Kettering Institute – research
- The diaphragm and pelvic floor work as a piston during the breathing. When we breathe in, the diaphragm moves down along with the pelvic floor and when we breathe out they both move up. Breathing mechanics is very important for pressure mechanics- that means it provides stability, keeps the organ continence, pelvic floor function, lymphatic draining, and reduces the strain on joints. The factors can affect the breathing mechanics
- Abdominal fascial restrictions
- Shallow breathing from pain
- Decreased mobility of fascia of diaphragm/pelvic floor
- The image is taken from Grey’s Anatomy
- The restriction of fascia can affect the circulation and lymphatic drainage. Many women have pelvic congestion and also swelling of vulva and itching.
How can Physical Therapy help?
Goals of Physical Therapy are
- Reduction of pain
- Improve posture
- Improve mobility of muscle/fascia and organ to improve biomechanics and movement of the body
- Improve circulation and lymphatic drainage
The Physical Therapist have to perform detailed evaluation on fascial mobility, joint mechanics, muscle guarding pattern, posture, any swelling or signs of congestion, bowel and bladder function, sexual function, pelvic floor muscle function, lumbar spine/sacroiliac joint mobility and stability, breathing mechanics, load transfer, and central sensatization. I have found great success with fascia mobilization on abdomen/chest wall/diaphragm, and around the abdominal organ/pelvic floor muscles to reduce pain, improve mobility, circulation, breathing mechanics, bowel/bladder function and overall well being.
About the author
The author of this article, Neha Golwala, PT, DPT is a vetted endometriosis physical therapist. With more than 10 years of experience, she works at Zuppa Physical Therapy P.C. in New York. Neha uses manual therapy techniques including myofascial release, joint mobs, and neurominetic energy. She is an expert in the development of posture awareness and connecting mind to body to recover from injuries and prevent injuries and improve performance.